Types of Breast Cancer
- Breast Cancer Overview
- Newly Diagnosed
- Signs & Symptoms
- Detecting & Diagnosing
- Types of Breast Cancer
- Hormone Receptor Status
- Staging
- Treatment Options
- Surgical Treatment Options
- Breast Cancer Recurrence
- Breast Reconstruction
- Risk Factors
- Genetics & Breast Cancer
- Breast Cancer FAQs
- Living as a Survivor
Did you know that breast cancer is not a single disease, but rather a broad term covering many different types of the disease? Therefore, your treatment plan may look completely different than another breast cancer patient’s treatment plan, all because of your specific breast cancer type.
Use this guide to learn more about the different types of breast cancer, how they are determined, and how they are classified.
After a breast cancer diagnosis, your cancer care team will need to determine your specific type of breast cancer. An in-depth assessment will be done on the breast tissue sample collected from your biopsy or the tumor after your breast cancer surgery. Several factors are looked at, including:
- How the breast cancer cells appear under the microscope
- Where the cancer cells originated
- The cancer cells reaction to hormones
- The breast cancer cells’ genetic/hereditary make-up
Breast Cancer Types
Breast cancer occurs in two broad categories: non-invasive and invasive. Breast cancer categorized as invasive (or infiltrating) means the disease has spread outside of the duct or lobule into the surrounding breast tissue. Noninvasive (or in situ) cancer, on the other hand, means that the cancerous cells are still confined to the breast duct or lobule.
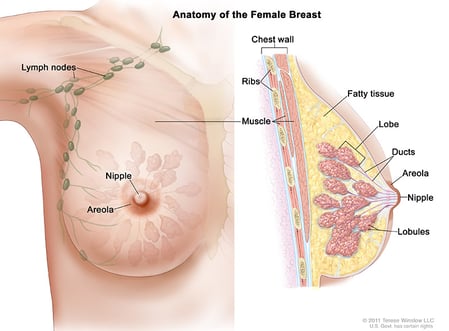 It is possible to have a combination of different cancer types within a single breast tumor. Also, where the cancer type is rare, a lump or tumor may never form at all.
It is possible to have a combination of different cancer types within a single breast tumor. Also, where the cancer type is rare, a lump or tumor may never form at all.
Common Categories Of Breast Cancer
Understanding the ins and outs of breast cancer can be difficult— especially when there are so many different types. We encourage you to speak with your breast cancer specialist at Willamette Valley Cancer Institute and Research Center so they can address any questions or concerns you may have.
Certain breast cancers are more common than others. Types of common breast cancers include:
Invasive ductal carcinoma
Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) means abnormal, cancer cells originated in the lining of the breast milk duct and have invaded surrounding tissues. Over time, IDC can spread to your lymph nodes along with other areas of your body. IDC accounts for approximately 80% of all breast cancers, making it the most common type of breast cancer.
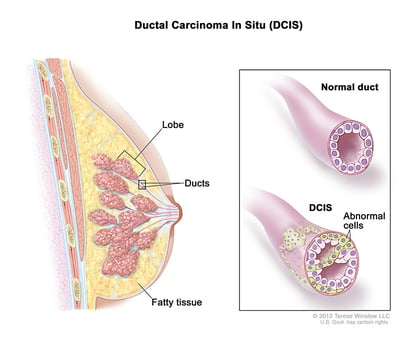
Ductal carcinoma in situ
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is non-invasive breast cancer. In DCIS, the abnormal cancer cells have been contained in the lining of the milk duct in the breast. DCIS isn’t considered life-threatening; however, it can increase the patient’s risk of developing invasive breast cancer later on. Most recurrences happen within 5-10 years after initial diagnosis.
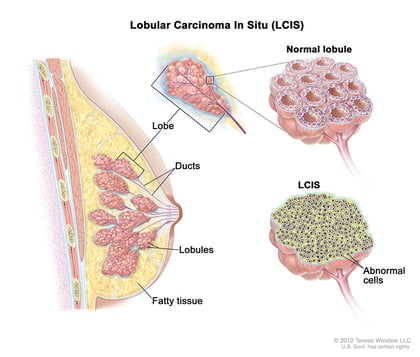
Lobular carcinoma in situ
Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) is sometimes called lobular neoplasia. Though the name can be misleading, LCIS is not considered cancer or pre-cancer because it doesn’t turn into invasive cancer if untreated. Instead, LCIS is an indication that a person is at an elevated risk of developing breast cancer later.
Invasive lobular carcinoma
Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) starts in the milk glands and can spread to other parts of the body. It is the second most common form of invasive breast cancer, accounting for 10 to 15% of breast cancer cases.
Invasive breast cancers will most likely require an oncology team to treat to create a breast cancer treatment plan using one or more of the following:
- Chemotherapy
- Hormone therapy
- Biologic therapy
- Radiation therapy
- Surgery
Less Common Types Of Breast Cancer
Inflammatory breast cancer
A less common type of breast cancer is inflammatory breast cancer (IBC). Inflammatory breast cancer accounts for 1-3% of all breast cancers. It often appears to be an infection (breast red, swollen, and inflamed), but it is cancer that blocks lymphatic vessels in the skin and breast tissue, causing a buildup of fluid (lymph).
Related Reading:
What is Inflammatory Breast Cancer?

Paget disease of the nipple
This type of breast cancer starts in the breast ducts and spreads to the nipple’s skin and then to the areola, the dark circle around the nipple. This type of breast cancer only accounts for about 1% of all cases of breast cancer.
Phyllodes tumor
Phyllodes tumors are rare breast tumors. These tumors develop in the connective tissue (stroma) of the breast and grow in a leaf-like pattern. Although phyllodes tumors tend to grow quickly, they rarely spread outside the breast.
Angiosarcoma
Angiosarcoma is cancer in the inner lining of blood vessels that can occur in any part of the body. This form of cancer rarely occurs in the breast.
Breast Cancer In Men
Although breast cancer more commonly affects women, it can affect men, too. Male breast cancer is a rare type of breast cancer that forms in the breast tissue of men. Typically, it is most common in older men, though it can occur at any age.
The most common types of breast cancer in men include ductal carcinoma in situ, invasive ductal carcinoma, and invasive lobular carcinoma. However, men can also develop some of the less common types of breast cancer listed above.
How Breast Cancer Type Affects Treatment
Breast cancer is not a one-size-fits-all disease. Therefore, neither are breast cancer treatment options. It is crucial to determine which hormones, if any, are involved in the growth of your breast cancer. Typically, your breast cancer treatment plan will be personalized based on your specific type, biomarkers, and stage of breast cancer.
Your WVCI breast cancer doctor will run some tests that indicate the hormone receptor status and HER2/neu (a protein found in some types of cancer cells) status of your breast cancer tumor. These results will play a significant role in the kind of breast cancer treatment we recommend.
