Breast Cancer Treatment Options in the Willamette Valley
Breast Cancer
When breast cancer is caught early, five-year survival rates are 99%, according to the American Cancer Society. But breast cancer is not just one specific disease; there are many different types. The treatment that’s best for one woman may not be best for another.
Thankfully, women with breast cancer have many more treatment options than ever before. Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and hormone therapies still play a role in breast cancer treatment, depending on a person’s breast cancer type, staging, and hormone status. Newer to the arena are targeted therapies, immunotherapies, and ongoing clinical trials.
Common Breast Cancer Treatments
Treatment options may include one or a combination of the following:
Surgery for Breast Cancer Removal
Surgery is the most common breast cancer treatment. Your breast cancer doctor can explain each type, discuss and compare the benefits and risks, and describe how each will change the way you look:
- Breast-sparing surgery: This is an operation to remove the cancer but not the breast. It’s also called breast-conserving surgery. It can be a lumpectomy or a segmental mastectomy (also called a partial mastectomy). Sometimes an excisional biopsy is the only surgery a woman needs because the surgeon removed the whole lump.
- Mastectomy: This is an operation to remove the entire breast (or as much of the breast tissue as possible). In some cases, a skin-sparing mastectomy may be an option. For this approach, the surgeon removes as little skin as possible.
Related Reading:
Should Surgery Be Done Before Other Breast Cancer Treatments?
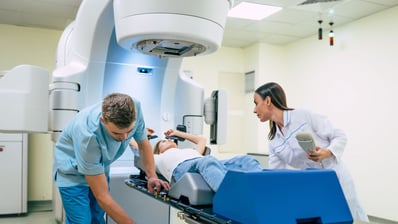
“Radiation treatment is much more elaborate than it was 20 years ago,” says Willamette Valley Cancer Institute radiation oncologist Dr. Emily Dunn.
Dr. Dunn says advances in technology, particularly in the last decade, have made radiation therapy more precise and individualized to each patient’s anatomy.
“For instance, we used to use X-rays to create a radiation plan and now we use a CT scan, which gives a three-dimensional view of the treatment area, allowing us to take into account not only how much radiation is going to the target area—the breast and possibly the surrounding lymph nodes—but also to the area we don’t want to target, including the heart and the lungs.”
“Patients often ask if the radiation hurts, and it doesn’t. What we’re treating you with is high-powered X-rays,” Dr. Dunn says. “You’re not going to feel the radiation treatment. You’ll hear the machine click on and off. You’ll notice you’re the only person in the room receiving treatment, but we can see you and hear you on our private screens and make sure everything is going well.”
As with most cancer treatments, radiation therapy can have side effects, which vary from patient to patient. Some breast cancer patients experienced discomfort under the armpit or close to the treatment site and some fatigue. Some patients may experience mild or intense skin irritation, similar to a sunburn.
Doctors use two types of radiation therapy to treat breast cancer. Some women receive both types:
- External radiation therapy: This is the most common type of radiation therapy used for breast cancer. A machine is used to aim high-energy rays (or beams) from outside the body into the tumor. You will go to a clinic for treatment. Treatments are typically given 5 days a week for 4 to 8 weeks.
- In some cases, hypofractionated radiation therapy treatments are used. This approach administers the same dose of radiation in a shorter time frame. Instead of one short session every weekday for 6-8 weeks, it’s possible to increase the dose per day to shorten the number of weeks that radiation therapy is needed. Some patients can be done with radiation within 4-5 weeks when hypofractionated therapy is used.
- Internal radiation therapy (implant radiation therapy or brachytherapy): The doctor places one or more thin tubes inside the breast through a tiny incision. A radioactive substance is loaded into the tube. The treatment session may last for a few minutes, and the substance is removed. When it’s removed, no radioactivity remains in your body. Internal radiation therapy may be repeated every day for a week.
What Happens During Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer?
Radiation oncologists, including Dr. Emily Dunn, explain what breast cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy can expect from treatment at Willamette Valley Cancer Institute.
Related Reading:
How is Radiation Therapy Used to Treat Breast Cancer?
Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. The drugs that treat breast cancer are usually given through a vein (intravenous) or as a pill. You’ll probably receive a combination of drugs.
You may receive chemotherapy in an outpatient part of the hospital, at the doctor’s office, or at home. Some women need to stay in the hospital during treatment.
Some anticancer drugs can damage the ovaries. If you have not gone through menopause yet, you may have hot flashes and vaginal dryness. Your menstrual periods may no longer be regular or may stop. You may become infertile (unable to become pregnant). For women over the age of 35, this damage to the ovaries is likely to be permanent.
On the other hand, you may remain able to become pregnant during chemotherapy. Before treatment begins, you should talk with your breast cancer specialist about birth control because many drugs given during the first trimester are known to cause birth defects.
Targeted Therapy for Breast Cancer Treatment
Some women with breast cancer may receive drugs called targeted therapy. Targeted therapies can be used to treat breast cancer based on the specific characteristics of cancer cells, such as a specific gene, protein, or tissue environment that allows the cells to grow quickly or abnormally.
For example, targeted therapy may block the action of an abnormal protein (such as HER2) that stimulates the growth of breast cancer cells.
In general, targeted therapies are often more effective, longer-lasting, and less toxic than other therapy options. Breast cancers are evaluated in the pathology lab to determine if they contain receptors - including HER2, estrogen receptors, or progesterone receptors. Researchers and oncologists now understand that being able to target a certain aspect of a tumor leads to better outcomes for the patient. Based on the findings in the pathology lab, oncologists are able to determine if the best treatment option is targeted therapy.
“Because a lot of times, those mutations are what’s driving the tumor—its growth, its replication, its resistance to dying,” says medical oncologist Dr. Jon Gross. “So, if we are able to shut that mutation off, then we can shut off that cancer.”
Types of Targeted Therapy Used for Breast Cancer
Two primary types of targeted therapy include:
- Monoclonal antibodies: block a specific target on the outside of cancer cells
- Small-molecule drugs: block the process that helps cancer cells multiply and spread
Targeted Therapy for HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
If lab tests show that your breast tumor has too much of a protein called human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), it is likely that your breast cancer will grow and spread more aggressively. Drugs have been developed to target this type of breast cancer.
Targeted Therapy for Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer
Treatment for breast cancer that is hormone receptor-positive will typically begin with hormone therapy. To make hormone therapy more effective, targeted therapy drugs have been developed.
Targeted Therapy for Women with BRCA Gene Mutations
Hereditary breast cancer syndrome caused by inherited gene changes in BRCA1 and BRCA2 will be targeted with a type of drug known as a PARP inhibitor.
For cancers that have no positive hormone receptors, including a subtype called triple-negative breast cancer, hormone therapy or targeted therapy is not helpful. Therefore, treatment for those types of breast cancer will often consist of a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation.
Read our blog to learn more: Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Why Is It Harder to Treat?
Hormone Therapy for Breast Cancer
Hormone therapy may also be called anti-hormone treatment. If lab tests show that the tumor in your breast has hormone receptors, then hormone therapy may be an option. Hormone therapy keeps cancer cells from getting or using the natural hormones (estrogen and progesterone) they need to grow.
Options Before Menopause
If you have not gone through menopause, the options include:
- Tamoxifen: This drug can prevent the original breast cancer from returning and also helps prevent the development of new cancers in the other breast. As treatment for metastatic breast cancer, tamoxifen slows or stops the growth of cancer cells that are in the body. It’s a pill that you take every day for 5 years.
In general, the side effects of tamoxifen are similar to some of the symptoms of menopause. The most common are hot flashes and vaginal discharge. Others are irregular menstrual periods, thinning bones, headaches, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, vaginal dryness or itching, irritation of the skin around the vagina, and skin rash. Serious side effects are rare, but they include blood clots, strokes, uterine cancer, and cataracts.
- LH-RH agonist: This type of drug can prevent the ovaries from making estrogen. The estrogen level falls slowly. Examples are leuprolide and goserelin. This type of drug may be given by injection under the skin in the stomach area. Side effects include hot flashes, headaches, weight gain, thinning bones, and bone pain.
- Surgery to remove your ovaries: Until you go through menopause, your ovaries are your body’s main source of estrogen. When the surgeon removes your ovaries, this source of estrogen is also removed. (A woman who has gone through menopause wouldn’t benefit from this kind of surgery because her ovaries produce much less estrogen.) When the ovaries are removed, menopause occurs right away. The side effects are often more severe than those caused by natural menopause. Your healthcare team can suggest ways to cope with these side effects.
Options After Menopause
If you have gone through menopause, the options include:
- Aromatase inhibitor: This type of drug prevents the body from making a form of estrogen (estradiol). Examples are anastrazole, exemestane, and letrozole. Common side effects include hot flashes, nausea, vomiting, and painful bones or joints. Serious side effects include thinning bones and an increase in cholesterol.
- Tamoxifen: Hormone therapy is given for at least 5 years. Women who have gone through menopause receive tamoxifen for 2 to 5 years. If tamoxifen is given for less than 5 years, then an aromatase inhibitor often is given to complete the 5 years. Some women have had hormone therapy for more than 5 years. See above for more information about tamoxifen and its possible side effects.
Immunotherapy for Breast Cancer
Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses a person’s own immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells by blocking certain proteins (checkpoints) that tumors use to hide. Breast cancer research has proven that immunotherapy improves outcomes for breast cancer patients.
Pembrolizumab, an immunotherapy drug, is a PD-1 inhibitor that boosts immune response. It is often used with chemotherapy to treat triple-negative breast cancer before or after surgery, cancer that has returned locally and cannot be surgically removed, or cancer that has spread beyond the breast. It’s given by IV every 3 to 6 weeks, and in some cases, testing for the PD-L1 protein can help determine if it’s effective.
Breast Cancer Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are carefully controlled research studies that test promising new therapies or procedures to advance cancer treatment.
Willamette Valley Cancer Institute and Research Center provide many investigational drugs through clinical trials, providing patients access to experimental treatments otherwise unavailable. If you’re interested in participating in a trial, your oncologist can help determine if you’re a candidate. To ensure safety, candidates are carefully screened.
Learn more about the latest developments in cancer research.
The Latest Treatments for Breast Cancer Available at Willamette Valley Cancer Institute
If you have been newly diagnosed with breast cancer, the first step is to schedule a consultation with a breast cancer doctor. At Willamette Valley Cancer Institute (WVCI), we offer personalized treatment plans, including the latest cancer treatments available, as well as second opinions.
Breast Cancer Specialists Caring for Patients in Willamette Valley and the Oregon Coast
WVCI breast cancer centers provide patients with the latest in breast cancer treatments. Select a location that is convenient for you to request a consultation with an oncologist.
